What is Phishing: How Online Scammers Trick You and Steal Information (Quick Guide)
Phishing is a cybercrime technique where attackers attempt to steal sensitive information by pretending to be a trusted organization or individual. Online phishing attacks can target anyone who uses email, messaging apps, social media, or even phone calls. Cybercriminals rely on deception and psychological manipulation to trick victims into revealing passwords, bank account numbers, or other personal information.
Phishing scams are evolving rapidly, and modern attacks are becoming more sophisticated. They are no longer limited to generic emails. Instead, attackers use highly targeted methods that exploit trust and familiarity. Understanding how phishing works and the different types of phishing attacks is essential to protect yourself, your business, and your online accounts.
Recognizing phishing attempts quickly can prevent identity theft, financial loss, or account takeovers. Phishing awareness, combined with effective security practices, is the best defense against these online threats.
Table of Contents
How Phishing Works?
Phishing attacks generally follow a predictable sequence. First, attackers prepare deceptive messages, emails, or fake websites that appear legitimate. Then, victims are lured to click links, download attachments, or enter personal information. Once the victim interacts, attackers capture credentials, install malware, or commit fraud.
Phishing often uses social engineering techniques, which manipulate emotions like fear, urgency, curiosity, or trust. Attackers carefully craft messages that look official, using logos, design elements, and language from real organizations. Even small inconsistencies can be clues to the scam.
How many types of phishing are there?
1.Email Phishing

Email phishing involves generic mass emails that attempt to trick recipients into clicking on malicious links or downloading infected attachments. These emails often pretend to be from banks, tech companies, or government agencies. Attackers exploit urgency, fear, or curiosity to make recipients act quickly.
Emails may include fake login pages, malware attachments, or prompts to verify personal information. Because email phishing targets a wide audience, attackers rely on volume and simplicity rather than personalization.
- Distinct Signs You Are a Victim of Email Phishing:
- Sender addresses that look suspicious or slightly altered
- Generic greetings like “Dear Customer”
- Urgent or threatening language demanding immediate action
- Links or attachments leading to untrusted websites
2.Spear Phishing
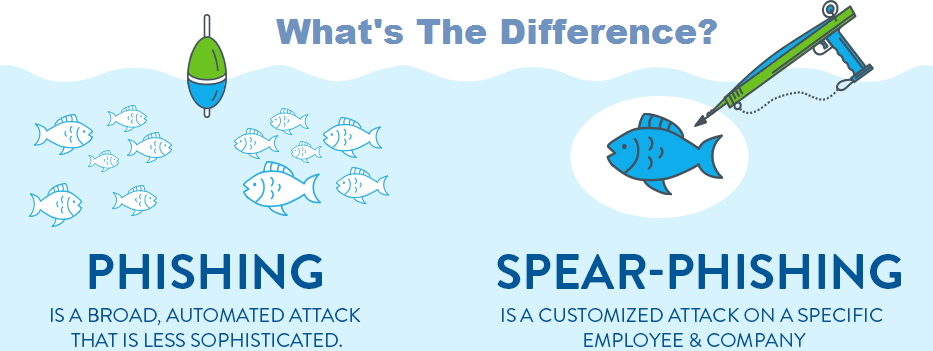
Spear phishing is a highly targeted email attack aimed at a specific person or organization. Attackers use personal details, such as the recipient’s name, job role, or recent activities, to appear credible. This type of phishing is often used to steal sensitive corporate information or credentials.
Spear phishing is more dangerous than standard email phishing because it relies on trust. Attackers can appear to be colleagues, partners, or managers, making detection difficult. Even small details, like mimicked email formatting, can deceive the recipient.
- Distinct Signs You Are a Victim of Spear Phishing:
- Personalized greetings with your name or job title
- References to work projects or internal communications
- Slightly altered email addresses from known contacts
- Requests that are unusual or out of character for normal communication
3.Whaling (CEO Fraud)

Whaling is a spear phishing variant targeting executives or high-level staff. Attackers craft emails that request wire transfers, financial authorizations, or sensitive information. Whaling is often disguised as legal notices, invoices, or urgent business directives.
These attacks can cause significant financial or reputational damage. Attackers spend time researching the organization and its decision-makers, using official branding and formal language to appear legitimate.
- Distinct Signs You Are a Victim of Whaling:
- Emails addressed to executives or senior staff
- Formal, professional tone with corporate logos
- Requests for high-value transactions or confidential info
- Follow-up calls or pressure to act immediately
4.Business Email Compromise (BEC)
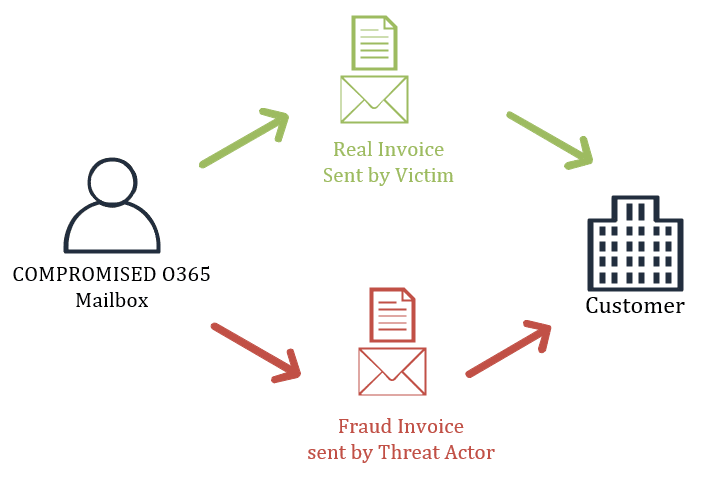
BEC attacks involve fraudulent emails impersonating colleagues, vendors, or partners to redirect funds or data. Attackers exploit trust and internal processes, often sending messages that appear completely legitimate.
These attacks are typically well-researched. The attackers may mimic writing style, signatures, and prior email formatting to make their message convincing.
- Distinct Signs You Are a Victim of BEC:
- Unexpected payment or account changes from a trusted source
- Emails requesting wire transfers without prior discussion
- Subtle changes in sender address or domain
- Urgency or insistence to bypass normal verification channels
5.Clone Phishing

Clone phishing occurs when attackers copy a legitimate email and replace links or attachments with malicious content. The copied email appears identical to the original, making recipients more likely to engage.
Clone phishing is effective because it exploits trust from previous legitimate communication. Victims may click links or open attachments believing the message is safe.
- Distinct Signs You Are a Victim of Clone Phishing:
- Emails look identical to previous communications
- Links or attachments slightly differ from original versions
- Unexpected instructions or new requests
- Sudden urgency that was not present before
6.Smishing (SMS Phishing)

Smishing uses text messages to trick users into clicking links or providing sensitive information. Messages often impersonate banks, delivery services, or official agencies. Mobile users are particularly vulnerable due to casual interaction with texts.
Attackers often rely on urgency, promising rewards or claiming an account problem. These attacks can lead to malware installation or stolen credentials.
- Distinct Signs You Are a Victim of Smishing:
- Messages from unknown numbers
- Links prompting immediate action
- Requests for personal info through SMS
- Shortened or disguised URLs
7.Vishing (Voice Phishing)

Vishing involves phone calls where attackers impersonate trusted entities. They may ask for login credentials, financial information, or authorization of transactions. Attackers use psychological pressure to prompt victims to comply.
Vishing can be conducted by automated calls or live impersonators. Many victims trust the caller because the message appears official.
A recent, widely reported case is the Geek Squad email scam, which begins with fake billing emails and evolves into voice phishing when victims call the “support” number listed. Scammers then use phone conversations to gain remote access or steal payments, proving how email and vishing tactics often merge into a single coordinated fraud.
- Distinct Signs You Are a Victim of Vishing:
- Calls asking for sensitive account details
- Threats of legal action or penalties
- Local-looking numbers that mimic legitimate contacts
- Urgent requests to act without verification
8.Angler Phishing (Social Media Phishing)

Angler phishing occurs on social media platforms, where fake support accounts or posts lure users to malicious websites. Attackers may pose as verified companies or representatives.
These scams exploit trust in social networks. Victims may reveal passwords or download malware believing the source is official.
- Distinct Signs You Are a Victim of Angler Phishing:
- Messages from unverified or recently created accounts
- Links directing outside the official platform
- Requests for login info or personal data
- Offers that seem too good to be true
9.Pharming
Pharming redirects users from legitimate sites to fraudulent ones, often via DNS poisoning or malicious scripts. Victims may not realize the site is fake and may enter sensitive information.
Pharming attacks often target banking or login portals. The fake websites look identical to the originals, making detection difficult.
- Distinct Signs You Are a Victim of Pharming:
- Strange URLs or slight misspellings
- Missing HTTPS or certificate warnings
- Unexpected redirects
- Login failures despite correct credentials
10.Watering Hole Attacks
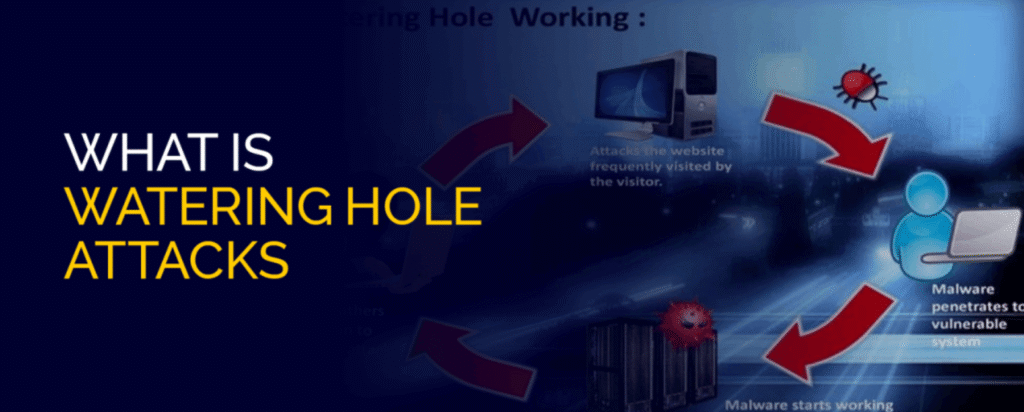
Watering hole attacks involve compromising websites frequently visited by a target group. Visitors may inadvertently download malware or have credentials captured.
Attackers carefully select sites relevant to their victims. These attacks are stealthy because the compromised site is trusted.
- Distinct Signs You Are a Victim of Watering Hole Attacks:
- Unexpected pop-ups or download prompts on trusted sites
- Browser slowdowns after visiting familiar websites
- Antivirus warnings triggered by normal browsing
- Redirects to unknown pages
11.Credential Harvesting Pages
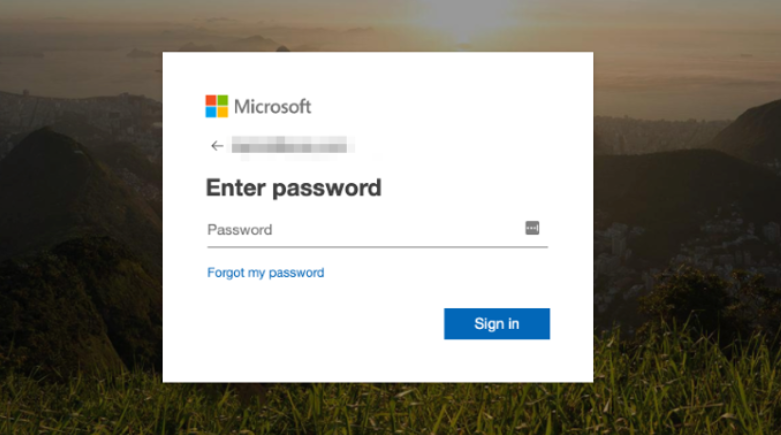
Credential harvesting pages are fake login portals designed to capture usernames and passwords. They often mimic banking, social media, or work login screens.
These attacks are distributed via email, SMS, or social media. Victims unknowingly provide sensitive information directly to attackers.
- Distinct Signs You Are a Victim of Credential Harvesting Pages:
- Login pages accessed via email or SMS links instead of bookmarks
- Slight differences in domain names
- Missing or suspicious HTTPS certificates
- Login errors despite correct credentials
12.QR Code Phishing

QR code phishing uses malicious QR codes that link to harmful websites or downloads when scanned. These attacks have increased due to contactless technologies.
Victims may trust QR codes from flyers, posters, or advertisements. Scanning without verification can expose users to malware or stolen credentials.
- Distinct Signs You Are a Victim of QR Code Phishing:
- QR codes redirecting to unfamiliar URLs
- Requests to download apps or files immediately
- Login prompts after scanning
- Non-secure website warnings
How to Recognize Phishing Attempts
Recognizing phishing attacks quickly can prevent data theft and financial loss. Key signs include:
- Misspelled email addresses or domains
- Messages with unusual greetings or lack of personalization
- Requests for passwords, PINs, or other confidential information
- Suspicious links or attachments
- Urgent or alarming language designed to provoke immediate action
How to Protect Yourself from Phishing
Protecting yourself from phishing requires vigilance and a combination of security practices.
- Verify the source: Check sender addresses and official websites before responding
- Use multi-factor authentication: Adds a layer of security even if credentials are compromised
- Keep software updated: Patch vulnerabilities in operating systems, browsers, and security tools
- Educate yourself and employees: Awareness reduces the likelihood of falling victim
- Use anti-phishing tools: Email filters, browser extensions, and security suites block malicious links and attachments
What is phishing, after all?
Phishing is a sophisticated form of online fraud that targets individuals and organizations alike. Email phishing, spear phishing, whaling, smishing, vishing, and clone phishing each have distinct methods and risks. Awareness of the signs, combined with proactive security practices, is essential to staying safe online. Vigilance, education, and protective tools are key defenses against phishing attacks.
FAQs
What is phishing and how does it work?
Phishing is an online scam where attackers trick users into revealing sensitive information through deceptive emails, messages, or websites.
How is spear phishing different from regular phishing?
Spear phishing is highly targeted and uses personal information to make the message appear legitimate.
Can phishing attacks happen via SMS or calls?
Yes, smishing and vishing are common forms of phishing through text messages and phone calls.
What should I do if I click a phishing link?
Immediately change your passwords, monitor accounts for suspicious activity, and report the incident.
Are phishing attacks limited to email?
No, phishing attacks can occur through email, SMS, phone calls, social media, and fake websites.



6 thoughts on “What is Phishing: How Online Scammers Trick You and Steal Information (Quick Guide)”